Learn why schools across the country are using dedicated K-12 cloud application security technology to protect students and staff
Many schools have adopted cloud technologies both in the classroom and administrative offices. Google for Education and Microsoft 365 are by far the two most used cloud applications in this market. And, while both have native security capabilities, they are limited or require expensive license upgrades to come close to the level of protection schools need. Until recently, K-12 cloud application security innovation had lagged behind the surge in cloud technology adoption.
Thus, the cloud application security industry was born. Officially dubbed Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) by Gartner, this (perhaps more recognizable name) is a bit of a misnomer. Because cloud application security does so much more than simply broker access to the cloud.
Cloud application security uses the app’s APIs to not only track access (information going into and being sent out of the app), but also monitors and reports on what is going on in the app once someone logs in. Cloud application security solutions are designed specifically to provide a strong level of visibility, control and protection of these types of applications and the data associated with them. Let’s dig in a little more…
What Cloud Application Security Does
Cloud application security is a fundamental control layer of cloud security. It’s primarily concerned with analyzing and controlling what is happening in your school’s web applications like Google G Suite, Google Drive, Office 365 Mail, OneDrive, SharePoint, Slack, Box, Dropbox and ShareFile.
Previous generations of cloud application security solutions use cloud gateways and proxies, which provide far less control of cloud application use. The new generation of cloud application security solutions connect directly into applications through an application programming interface (API), effectively integrating powerful security features into the application.
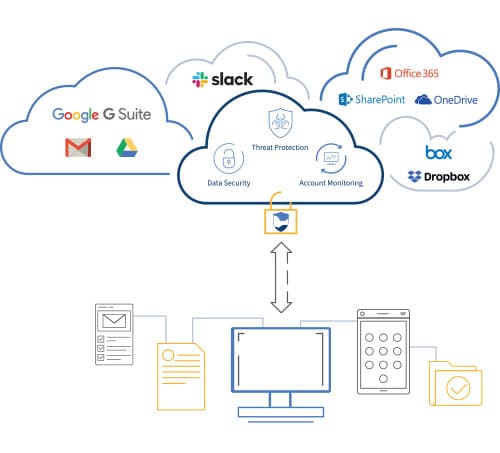
Cloud application security solutions provide school IT administrators with three key functions:
Visibility
Cloud application security provides K-12 IT teams with visibility into what’s going on within the cloud application. This gives you the ability to know who is doing what within the applications, as well as what information and images are being sent, received, stored, shared or viewed.
Control
System admins in K-12 school districts that use a cloud application security platform gain control over activities and behavior, driven by policies. This includes the ability to detect, alert on, and block activities that violate relevant regulations and school policies.
Protection
K-12 school IT systems are increasingly targets of malware and phishing schemes. A cloud application security platform protects systems against ransomware, malware, phishing, and other threats. Schools must be able to protect against threats that can lead to data loss, theft or corruption or the disruption of school operations such as through ransomware. Protection features often include threat detection, data loss prevention, and active monitoring of user behaviors.
[LEARN MORE] Free Cloud Application Security & Safety for K-12 School Districts Guide >>
Examples of Cloud Application Security Vendors
The leading cloud application security vendors that cater to the education market are:
- ManagedMethods
- SysCloud
- Palo Alto (Aperture)
Examples of Issues Cloud Application Security Addresses for K-12 Schools
- All uploaded files and incoming email messages and attachments are screened for phishing, malware and other threats. Messages and files are quarantined if a threat is found.
- All emails and attachments are scanned for keywords that indicate some sort of risk; for example, “suicide,” “bomb” or “gun.” Administrators can be alerted if a potential risk is uncovered.
- Content that is being sent outside the school network is screened for specific words, phrases or patterns to prevent sensitive data from leaving the school environment.
- Schools have the ability to implement policy scanning to ensure that the data security and student privacy aspects of regulations such as CIPA, COPPA, HIPAA, and FERPA, among others, are maintained in order to prevent compliance violations.
Example Cloud Application Security Use Cases for K-12 Administrators
- A student attempts to upload pornographic images to his Google Drive account with the intention of sharing them with his classmates for the shock value. The cloud application security system can detect the illicit images, revoke the file share upload and alert an IT administrator.
- A school nurse attempts to share a student’s medical record to a local clinic. This violates a HIPAA regulation and the file share is revoked and a warning message sent.
- An email message containing a phishing link has been sent to faculty members of a school. The cloud application security system identifies the threat inside the original message and quarantines the message before it can be distributed to the intended recipients.
- Three students form a suicide pact and share their plans using their school email accounts. The cloud application security system detects the keywords such as “take my own life” and “suicide” and alerts school authorities.
[LEARN MORE] Free Cloud Application Security & Safety for K-12 School Districts Guide >>
Limitations of a Cloud Application Security Solution
Cloud application security technologies don’t inspect content posted to social media or sent via direct messaging apps, which is where students are likely to conduct bullying campaigns, exchange “sext” messages, express threats against other people or the school, or reveal suicidal thoughts. Moreover, cloud application security doesn’t do anything at the device level, just at the cloud application level.
K-12 cloud application security should be an integral component of your school’s information security tech stack. Many school IT administrators are making the move to gain critical visibility into not just their file sharing tools but also email communications, while still protecting students and staff from malware and phishing scams. Learn how you can, too, with a free 30-day trial of ManagedMethods.

