Everything You Need to Know About Cloud Computing Security
Cloud computing security is the only way to keep your data stored safely in the cloud. Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving and becoming more common. Many security professionals mistakenly believe that their firewall or web filter is sufficient enough to secure information stored and shared in cloud applications. Or, worse yet, they believe the application service provider is responsible for securing their data.
Here, we’re going to take a look at what cloud computing is and why securing it is different from traditional network security.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Dictionary.com defines cloud computing as:
“The practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.”
Cloud computing allows organizations to store their business data in a cloud-based platform, rather than on a local or on-premise server. Switching to cloud computing alleviates the need for costly hardware and outsources server maintenance and security to some of the world’s most secure providers, such as Google, AWS, etc.
Cloud computing also improves business outcomes through increased productivity and collaboration. Employees, students, contractors, and other users can easily access files at any time, from anywhere, on any device. Cloud computing has been a driving force behind today’s untethered global workforce. It allows people to work, communicate, and collaborate from almost anywhere, eliminating the requirement for hiring and/or working locally.
The public cloud allows business owners to forgo heavy investments in hardware or software that break and become outdated quickly. Instead, they pay a subscription to their cloud provider, usually on a monthly or annual basis.
To further understand cloud computing, let’s delve into the different types below.
Public Cloud / SaaS
The most popular form of cloud computing is the public cloud, this is where most SaaS (software as a service) applications are hosted. The public cloud is a software distribution model that hosts the applications and makes them accessible to customers online through a web browser. G Suite and Microsoft Office 365 are examples of commonly used SaaS applications. This form of cloud computing will generally give users a more extensive configuration, which helps them create and code their own environment.
Private Cloud
The private cloud is designed to be used by a single organization. The organization can build and manage the underlying cloud infrastructure, making the private cloud the best data center automation tool for administrators. All of the computing resources can be secluded and delivered through a secure and private network, rather than with clients, customers, or outside organizations.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud, also referred to as the multi cloud, is a combination of both the private and public cloud. The hybird cloud allows users to create an environment where applications can be moved from the private cloud to the public cloud and vice versa. This then allows for data and workloads to be transfered from private to public clouds, giving users and business owners an extensive data deployment solution and therefore more flexibility.
How Is Cloud Computing Security Different?
While cloud computing is not inherently insecure, it does require a different security approach. This is particularly true for public and hybrid cloud infrastructures.
When moving to the cloud, IT managers will find that much of the visibility and control they used to have with on-premise network servers has been lost. Cloud computing security is unique mainly because there is no perimeter in the cloud, it is known as security without boundaries.
Bruce Sussman’s provocative SecureWorld article, Cybersecurity Perimeter Defense: Is the Concept Dead?, highlights this point particularly well. The article maintains that models designed for a static, enclosed environment are no longer relevant due to BYOD and cloud computing.
Sussman suggests that cloud computing requires a data-centric approach to cybersecurity, rather than a perimeter-centric approach. In other words, security professionals need to focus on the fundamental problem of keeping data safe, rather than simply stopping hackers, malware, etc. at the perimeter.
Data is valuable to hackers, but not all data is created equal. Organizations need to first categorize their types of data, then invest in strong defense tools to properly store and protect it. This security need gave rise to a segment of cybersecurity tools that have since been categorized as cloud access security brokers, or CASB.
What Is API Cloud Security?
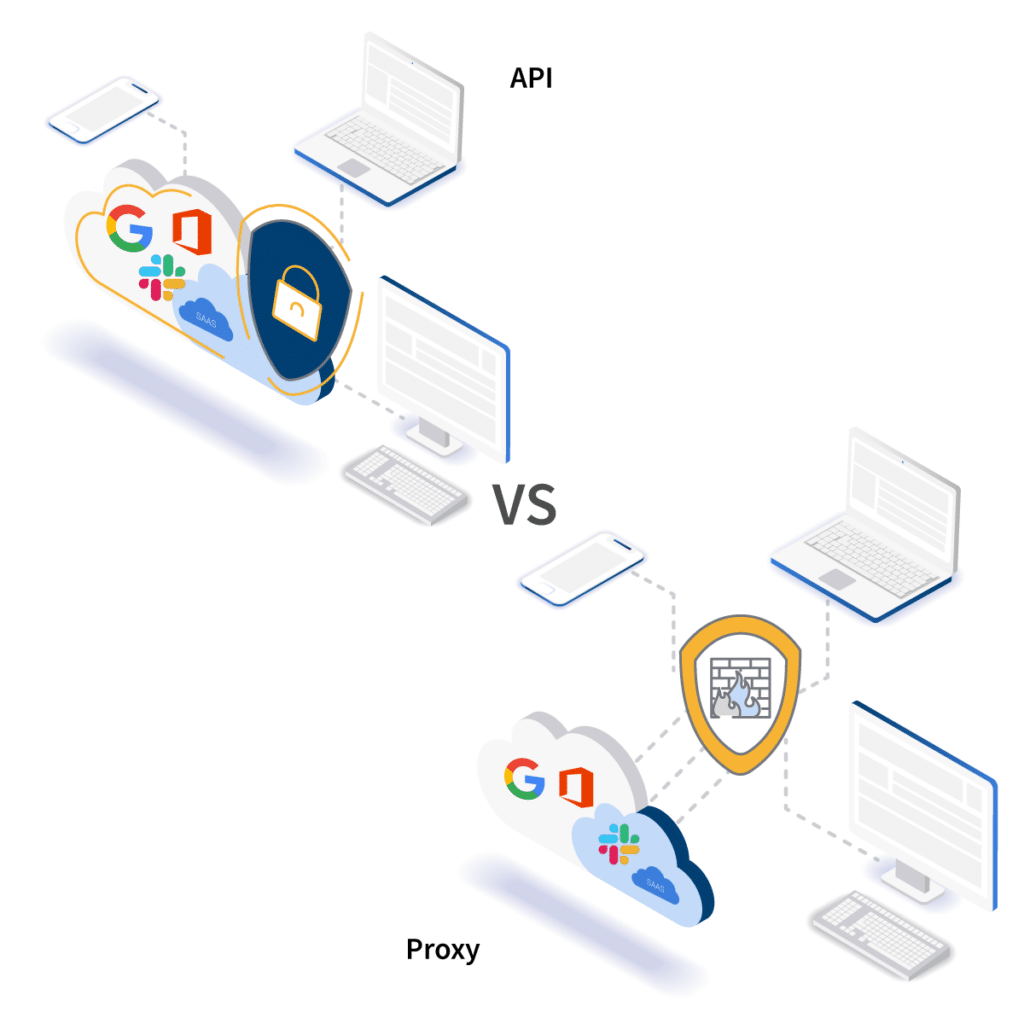
API cloud computing security is critical for teams using the public cloud and popular SaaS applications (think G Suite, Office 365, Slack, Dropbox, etc.). Third party vendors use APIs to build features that secure cloud applications in a way that works almost as an native function to application.
There are significant differences between an API and a proxy based CASB architecture. API-based security performs as though it is native to the application while proxies put a gateway between traffic and the application. Proxy-based security vendors may use a browser extension, agents, gateways, etc. as well as different terminology or tools.
At the end of the day, these tools work basically the same and they aren’t supported by most (if any) cloud applications. The fact that cloud service providers, including both Google and Microsoft, do not support or recommend the use of third party proxy-based cloud security solutions should not be taken lightly. This means that any time either company makes an update to their platform and/or infrastructure it could break the proxy’s settings, leaving your data vulnerable. Because API-based cloud computing security works with these applications’ native APIs, this issue does not occur.
Cybercriminals can circumvent proxy-based cloud security tools the same way they do firewalls and other perimeter-centric security. Proxy-based cloud security tools just duplicate the firewall you have set up in your network and place it in the cloud. API-based cloud security, on the other hand, adds a new layer of security to your stack that specifically monitors data and behavior in cloud applications. This provides IT managers with greater visibility and control over what data is being accessed by who, from where, and what is being done with it.
The cloud revolution isn’t coming, it’s here. Whether your organization has already made the move to the cloud or you’re planning one now, your IT and/or security team need to take the proper steps to ensure that the data stored, accessed, and shared in the cloud is secure.
ManagedMethods provides a complete, API-based cloud security solution to help protect your data and applications. Our solution works to prevent data breaches, malware and phishing threats, and account takeovers. Take control of your company’s information all in one easy-to-use, affordable platform.

